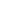
Hello . Your site is very useful. We have two ranges in the attachment. In the first range, the four columns are completely full and in the second range, the last column is empty. What is the 9000 number recognition algorithm? The p .Code & SRC columns are exactly equal, and we need to move the corresponding rate to the second range after finding the date that is less than or equal to the date in the first range, as you can see in the example.
(Here is the solar date or Persian and the "/" sign is removed from the year, month and day to be numbered [Explanation: Microsoft Office does not support solar date]). I want this issue to be resolved using PowerQuery. Because I can do it in VBA
If you have Excel for MS365 or 2021 you can fairly easily use a formula based solution with INDEX and XMATCH. But, you explicitly asked for a PQ based solution. The attached file contains both. See which one works best for you.
Hi Riny,
Thanks for helping out. Please try uploading your file again. You need to click the 'Start Upload' button after selecting your file, then wait for the grey check mark beside the file size before clicking the Submit Reply button.
Thanks,
Mynda
Thanks Mynda for pointing that out. Must have missed that last click.
Trying again.
Hello again . Thank you very much for your reply, Mr. Riny van Eekelen. And of course the site staff who have provided this opportunity.I may not have used the right words to say thank you. I use Google Translator to write
I wanted to ask members to write other ways to solve the problem
The following code is exactly what I wanted. A friend like Mr. Riny van Eekelen helped me get this code
let
//Read in the lookup table
Source = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Table1"]}[Content],
lookupTable = Table.TransformColumnTypes(Source,{
{"Date", Int64.Type},
{"P.Code",Int64.Type},
{"SRC", Int64.Type},
{"Rate", Int64.Type}
}),
//read in data table
Source2 = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Table2"]}[Content],
typeIt2 = Table.TransformColumnTypes(Source2,{
{"Date", Int64.Type},
{"P.Code", Int64.Type},
{"SRC", Int64.Type}
}),
//Join the two tables based on PCode and Src
join = Table.NestedJoin(typeIt2,{"P.Code","SRC"},lookupTable,{"P.Code","SRC"},"Joined", JoinKind.LeftOuter),
//for each joined subtable
// Sort descending
// Select only those rows where the date in table 2 is >= the corresponding date from table 1
// Then extract the first row Rate value (as that will be the closest to the date in table 2)
#"Added Custom" = Table.AddColumn(join, "Rate1", each Table.SelectRows(Table.Sort([Joined],
{"Date",Order.Descending}),(t)=> t[Date] <= [Date])[Rate]{0}, Int64.Type),
//Remove unneeded join table column
#"Removed Columns" = Table.RemoveColumns(#"Added Custom",{"Joined"})
in
#"Removed Columns"